The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security standards developed by Visa, MasterCard, JCB, Discover, and American Express in 2004. The Security Program, managed by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC), is designed to protect online and offline credit and debit card transactions from data theft and fraud.
Although PCI SSC does not have legal authority, any company performing credit or debit card transactions is expected to comply with the PCI DSS standard. PCI certification is seen as the safest way to protect confidential data and information while helping businesses build long-term, trust-based relationships with their customers.
See Also: PCI DSS Control Objectives
Compliance with PCI DSS shall be assessed annually or periodically by the Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) firm authorized by PCI SSC. The Attestation of Compliance (AOC) may also be carried out by the Internal Security Assessor (ISA) for companies processing large volumes. Companies may declare compliance by completing a Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) based on their credit and debit card transaction types and numbers.
The PCI DSS evaluates your card data and transactions with a set of requirements provided by the PCI SSC and specifies their compliance with the standard. A PCI DSS certified company is a valuable asset for consumers because it has documented its compliance with the PCI DSS standard and has documented that it safely processes credit cards under the standard.
See Also: What are the PCI DSS Audit Requirements
On the other hand, the monetary and reputational incompatibility risks that may arise in the event of any data leakage should be sufficient to convince any company owner to take data security seriously.
Stealing or leaking sensitive customer information will have serious implications for companies. Payment card providers also fine companies that commit such infringements. This situation causes a decrease in company revenues, and the reputation of the companies is severely damaged.
After a breach of card data, companies may not process credit cards or be forced to pay more additional costs than the initial cost of PCI security compliance. This is why PCI compliance is a continuous and secure way to ensure the security of payment systems and protect sensitive data.
Since its inception, PCI DSS has undergone several revisions to keep up with developments in the cyber threat environment. While basic PCI compliance rules remain constant, new requirements are regularly introduced based on cybersecurity and information security changes.
History of PCI DSS
The latest version of PCI DSS, released in March 2022, is 4.0. The PCI DSS 4.0 version contains 12 requirements in 6 prime objectives and contains approximately 400 control items.
The history of the PCI DSS version is as follows;
- PCI DSS version 1.0 was released on December 15, 2004.
- PCI DSS version 1.1 was released in September 2006.
- PCI DSS version 1.2 was released on October 1, 2008.
- Version 1.2.1 of PCI DSS was released in August 2009.
- PCI DSS version 2.0 was released in October 2010.
- PCI DSS version 3.0 was released in November 2013.
- PCI DSS version 3.1 was released in April 2015.
- The PCI DSS version was released on April 3, 2016.
- PCI DSS version 3.2.1 was released in May 2018.
- PCI DSS version 4.0 was released in March 2022.
See Also: What’s New in PCI DSS v4.0?
PCI DSS Requirements
PCI DSS applies to all companies which accept, process, and transmit payment cards. PCI SSC has a total of 12 requirements to manage cardholder data and provide a secure infrastructure securely. For the organization to be PCI compliant, more than 400 testing procedures must be carried out following 12 PCI requirements.
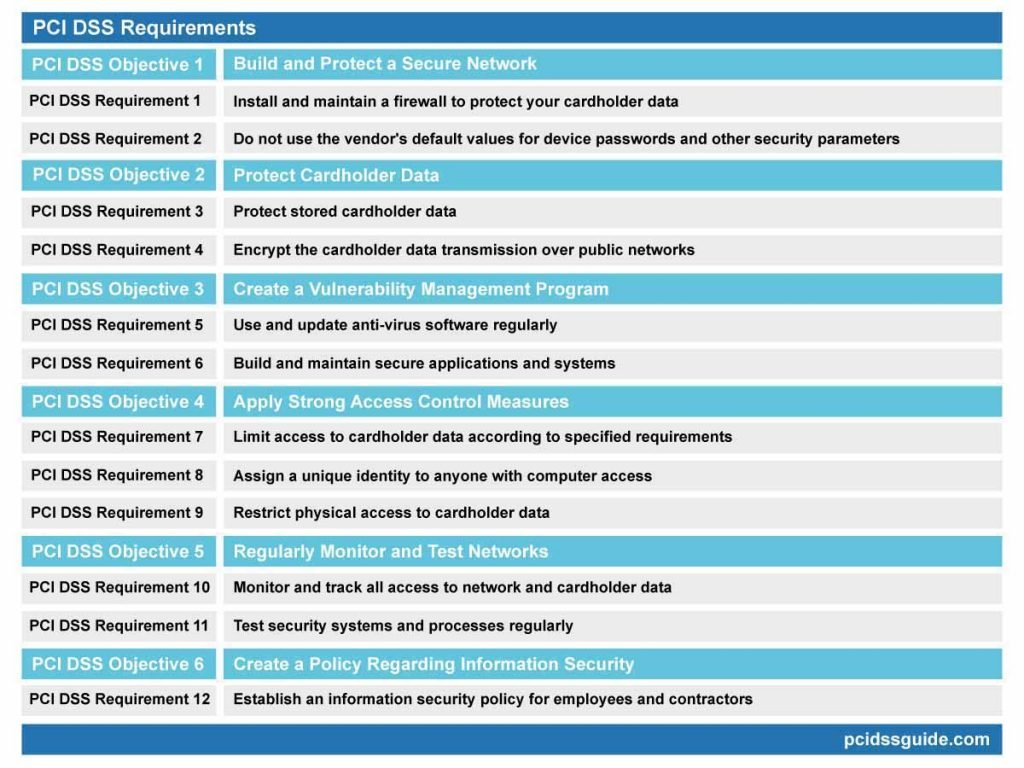
For detailed information about PCI DSS requirements, you can review our “PCI DSS Requirements” Article.
Below are general descriptions of the PCI DSS requirements:
PCI DSS Objective 1: Build and protect a secure network
PCI DSS Requirement 1: Install and maintain a firewall to protect your cardholder data.
See Also: PCI DSS Requirement 1 Explained
The first requirement of PCI DSS is to use firewalls to protect your card data environment. Correctly built firewalls preserve the environment around your card data. Firewalls limit incoming and outgoing network traffic according to the rules and requirements created by your company.
PCI DSS Requirement 2: Do not use the manufacturer’s default values for device passwords and other security parameters.
See Also: PCI DSS Requirement 2 Explained
Devices such as routers, firewalls, or POS systems have standard factory settings, such as usernames and passwords. Default settings and values make it easy to set up and support your device, but this also means that each model or version has the same username and password. Default passwords are easy to guess, and most of them are available on the Internet.
PCI DSS Objective 2: Protect Cardholder Data
PCI DSS Requirement 3: Protect stored cardholder data.
See Also: PCI DSS Requirement 3 Explained
The data stored on the card must be encrypted using algorithms accepted by the industry. Also, the encryption of card data is not sufficient. It is also necessary to securely protect the encryption keys.
PCI DSS Requirement 4: Encrypt the cardholder data transmission over public networks.
See Also: PCI DSS Requirement 4 Explained
If you transfer cardholder data over open, public networks, you must use encryption and enforce security policies accordingly. Encryption and authentication standards must be strong enough, and wireless networks must be correctly set up because unauthorized users can easily exploit vulnerabilities to access the Cardholder Data Environment (CDE).
PCI DSS Objective 3: Create a Vulnerability Management Program
PCI DSS Requirement 5: Use and update anti-virus software regularly.
See Also: PCI DSS Requirement 5 Explained
It is essential to install anti-virus software on all systems that are often affected by malware. It is necessary to ensure that anti-virus or anti-malware programs are updated regularly to detect known malware.
PCI DSS Requirement 6: Build and maintain secure applications and systems
See Also: PCI DSS Requirement 6 Explained
Quickly applying software updates is the key to application and system security. Applications are never flawless, and developers often release a variety of patches to fix security vulnerabilities. Once attackers understand that they can exploit vulnerabilities, they will forward this information to different hacker communities and misuse it until this vulnerability has been addressed.
PCI DSS Objective 4: Apply Strong Access Control Measures
PCI DSS Requirement 7: Limit access to cardholder data according to specified requirements.
See Also: PCI DSS Requirement 7 Explained
Robust access controls are designed to implement strict firm-defined measures to control access to the card data environment. The Role-based Access Control (RBAC) system should be used for accessing card data and systems, and access should be defined according to the “need to know” principle. Only authorized persons and systems are thus intended to access the data medium of the card.
PCI DSS Requirement 8: Assign a unique identity to anyone with computer access
See Also: PCI DSS Requirement 8 Explained
User IDs and passwords must also be unique and complex enough. Do not use group or shared passwords. A unique username and password must be created for each user, and this information should not be shared between users. No matter how strong a password is, it should not be considered unbreakable. A multi-factor authentication (MFA) mechanism should be installed in all non-console administrative access to systems.
PCI DSS Requirement 9: Restrict physical access to cardholder data.
See Also: PCI DSS Requirement 9 Explained
You must restrict physical access to the cardholder data environment, such as the data center, and record who has access to it. You also need to implement automatic server locking and timeout systems and check all devices annually. Most importantly, you should regularly train your staff on policies, procedures, and social engineering attacks related to physical security.
PCI DSS Objective 5: Regularly monitor and test networks
PCI DSS Requirement 10: Monitor and track all access to network and cardholder data.
See Also: PCI DSS Requirement 10 Explained
System event logs are information generated by systems such as firewalls, computers, or applications. You should keep and review the event logs produced by all PCI in-scope devices, servers, and applications.
However, these event logs will only be useful when reviewed. So you need to check the event logs daily to find or notice errors, abnormalities, and suspicious activity that deviate from the standards.
Daily monitoring systems, such as Security Information and Event Management Tools (SIEMs), help you monitor network activity, review device events, warn against suspicious activity, and keep user actions up-to-date.
PCI DSS Requirement 11: Test security systems and processes regularly.
See Also: PCI DSS Requirement 11 Explained
Vulnerabilities in web servers, web browsers, e-mail clients, POS applications, operating systems, and application interfaces can make your data vulnerable. You should find vulnerabilities by testing your systems regularly. To do this, you should perform vulnerability scanning and penetration tests on your PCI in-scope systems regularly.
PCI DSS Objective 6: Create a policy regarding information security
PCI DSS Requirement 12: Establish an information security policy for employees and contractors.
See Also: PCI DSS Requirement 12 Explained
Your company should establish documents, policies, and procedures relating to security practices and information security. You should also conduct a systematic risk analysis and assessment that identifies your critical assets and identifies their risks and weaknesses.
What are the PCI DSS Compliance Levels?
PCI compliance levels are divided into four groups, depending on the annual amount of merchant’s credit card, debit card, and prepaid card transactions. There are two service providers’ levels, depending on the annual amount of credit card, debit card, and prepaid card transactions. The PCI DSS, Compliance level classification, defines what an organization should do to remain compliant with the PCI standard.
See Also: PCI DSS Compliance Levels in Detail
All companies and service providers under the PCI DSS are required to perform an annual PCI DSS audit, although their requirements vary depending on the level of compliance. They should also have a quarterly external network scan (ASV scan) and document the PCI DSS Attestation of Compliance (AOC) form.
- Merchants are institutions that accept credit card payments for the goods and services they sell. These merchants are responsible for compliance with PCI DSS, even if they process payment cards through third party companies.
- Service providers are organizations that directly participate in and process cardholder data on behalf of another company.
Four levels of PCI compliance categorize merchants by credit, debit, and prepaid card processing over 12 months. It should not be forgotten that if a merchant encounters a breach that reveals card data, it can be upgraded to a higher compliance level.
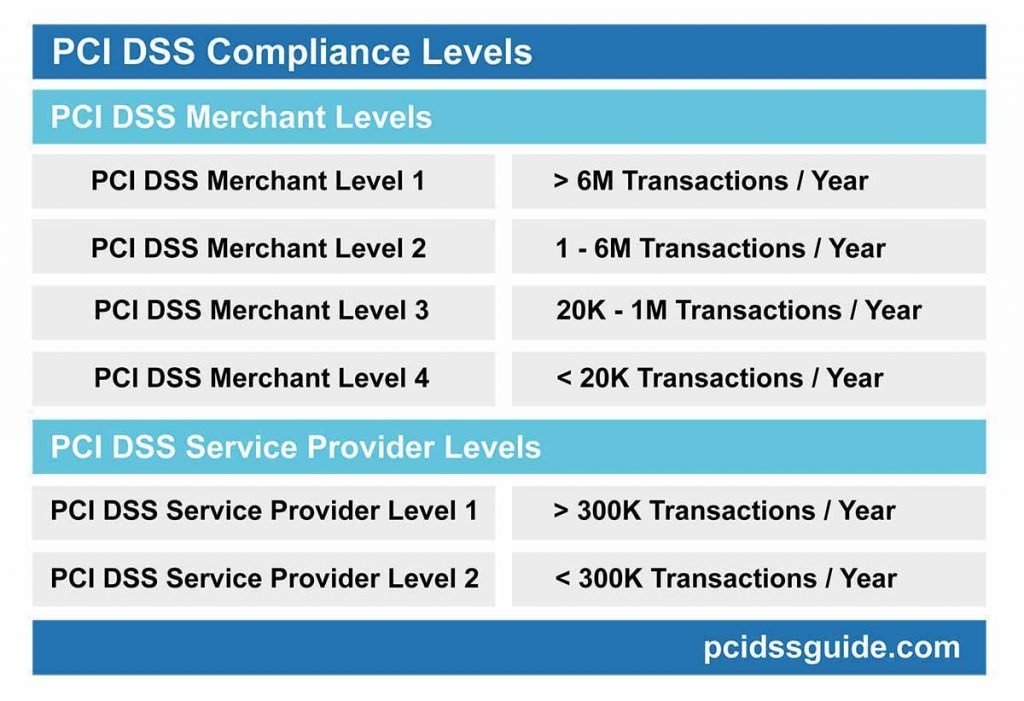
PCI DSS Compliance levels for merchants are as follows;
- PCI DSS Merchant Level 1: Merchants that perform more than 6 million card transactions annually.
- PCI DSS Merchant Level 2: Merchants that process between 1 and 6 million cards annually.
- PCI DSS Merchant Level 3: Merchants that process between 20,000 and 1 million cards annually.
- PCI DSS Merchant Level 4: Merchants that perform less than 20,000 card transactions annually.
Two PCI compliance levels categorize service providers by credit, debit, and prepaid card processing over 12 months.
The level of PCI DSS compliance for service providers is as follows;
- PCI DSS Service Provider Level 1: Service Providers performing more than 300,000 card transactions annually.
- PCI DSS Service Provider Level 2: Service Providers who process less than 300,000 card transactions annually.
What is the PCI DSS Audit? What are the PCI Compliance Requirements?
The PCI DSS audit consists of an External QSA (Qualified Security Assessor) or an ISA (Internal Security Assessor) for a Level 1 organizations.
As a result of the PCI audit, if the company is determined to comply with the PCI DSS standards, the ROC and AOC Compliance Reports shall be issued by the PCI QSA or ISA, demonstrating the company’s compliance with the PCI DSS standard.
See Also: PCI Compliance Reports: What Do SAQ, AoC, and RoC Mean?
These reports formally document the company’s compliance with the PCI DSS, and the report is valid for one year. The company must be re-audited before the date of the report’s validity, and the PCI DSS compliance report must be renewed.
PCI Level 1 service providers should conduct on-site PCI audits annually, submit ROC and AOC report, and provide quarterly network scans performed by the PCI Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV) four times a year.
PCI Level 2-4 organizations can document their compliance by filling out the PCI SAQ form (Self-Assessment Questionnaire) instead of external audits. However, these companies should also perform quarterly, four in total per year, network scans performed by the PCI Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV).
If deemed necessary, ROC and AOC reports may be requested by the bank or authorized institutions by demanding on-site audits of PCI level 2-4 merchants.
Likewise, PCI Level 2 service providers can document their compatibility by filling out a PCI SAQ form (Self-Assessment Questionnaire) instead of external audits. Also, Level 2 service providers must provide quarterly, four per year, network scans performed by the PCI Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV).
Banks or authorized organizations may request ROC and AOC reports by requesting on-site PCI audits for PCI Level 2 service providers where they deem it necessary.
There are a total of four PCI compliance reports and forms to be acquired by merchants and service providers, as follows;
- Report on Compliance (ROC) – This is a report by PCI QSA indicating compliance control substances resulting from an on-site audit.
- Attestation of Compliance (AOC) – This is an approved PCI QSA report indicating compliance resulting from an on-site audit.
- Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV) Scan Report – An external network vulnerability scan report issued by ASV firms approved by PCI SSC.
- Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) Form – This is how companies assess compliance with PCI on their own. Firms have different types of SAQ forms depending on their type of card transaction.
PCI DSS requirements for merchants are as follows;
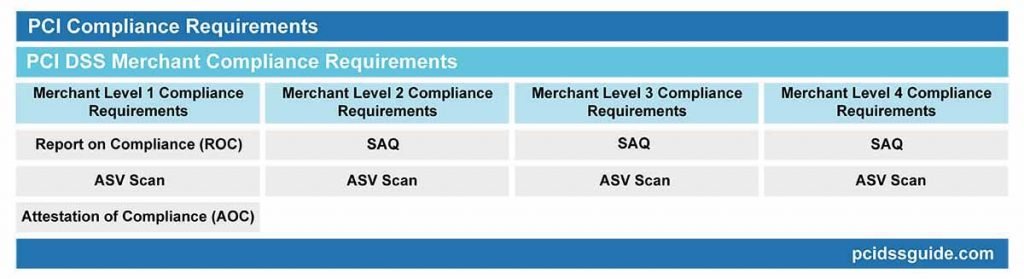
PCI DSS Merchant Level 1 Compliance Requirements
- Report on Compliance (ROC) – A Qualified Security Assessor (PCI QSA) or an Internal Security Assessor (ISA) signed by the company representative must be issued. (This is generally referred to as on-site PCI DSS audit.)
- A total of four network scans were performed quarterly by the PCI Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV).
- Attestation of Compliance (AOC) report.
PCI DSS Merchant Level 2 Compliance Requirements
- Annual Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) Form.
- A total of four network scans were performed quarterly by the PCI Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV).
PCI DSS Merchant Level 3 Compliance Requirements
- Annual Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) Form.
- A total of four network scans were performed quarterly by the PCI Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV).
PCI DSS Merchant Level 4 Compliance Requirements
- Annual Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) Form.
- A total of four network scans were performed quarterly by the PCI Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV).
Requirements for service providers based on the level of PCI DSS are as follows;
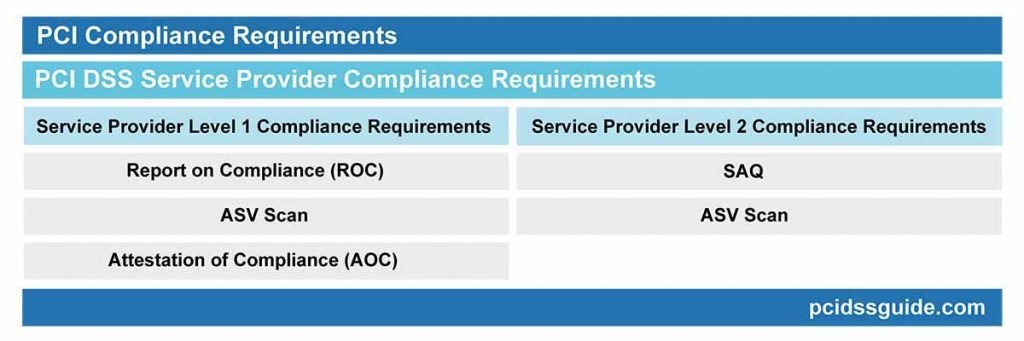
PCI DSS Service Provider Level 1 Compliance Requirements
- Report on Compliance (ROC) – A Qualified Security Assessor (PCI QSA) or an Internal Security Assessor (ISA) signed by the company representative must be issued. (This is generally referred to as on-site PCI DSS audit.)
- A total of four network scans were performed quarterly by the PCI Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV).
- Attestation of Compliance (AOC) report.
PCI DSS Service Provider Level 2 Compliance Requirements
- Annual Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) Form.
- A total of four network scans were performed quarterly by the PCI Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV).
What Happens If You Fail To Comply With PCI DSS?
Although PCI DSS is not a law, it is being implemented through contracts between companies, banks, and payment brands. Several possible consequences may result from non-compliance with PCI DSS compliance requirements;
See Also: What are the PCI Compliance Fines and Penalties?
- Penalties – PCI regulators can impose hefty fines on companies in the event of card data being stolen or leaked.
- Suspending credit card transactions – PCI regulators can forbid you to accept credit card payments and prevent you from using your existing card payment systems in the event of a data breach.
- Mandatory forensic analysis – You may need to undergo an expensive and time-consuming forensic examination.
- GDPR – Failure to report personal information violations within 72 hours under GDPR will result in severe fines.
- Liability for fraudulent transactions – You may be liable in a fraud case if your client’s sensitive data is leaked.
- Credit card replacement costs – Credit card issuers can reflect the cost of reprinting and editing credit cards.
- Notification and credit monitoring – You may need to inform your customers about security breaches and provide credit monitoring services to affected customers.
- Re-evaluate PCI compliance – You may need to undergo a full PCI DSS on-site audit to regain the ability to accept credit cards.
It should be noted that compliance with the PCI DSS standard does not mean that your systems are 100 % secure. It sets out the fundamental security controls to be observed for PCI DSS card data security. Therefore, applying PCI DSS controls appropriately as part of your regular business activities and, as defined by your overall security strategy, will increase your level of security.
Besides, PCI DSS security requirements may be used in other sensitive data and items that may require protection outside the PCI DSS of your organization, other than protecting payment card data. However, although PCI DSS compliance will increase your overall security level if adequately maintained, it should not replace a comprehensive and enterprise-wide security program.
For detailed information, see the PCI DSS Quick Reference Guide from the PCI SSC Documentation library.



Thank you so much. That would be really helpful if you can also create the practical steps
Thank you for this.
Appreciate the post, thanks.
A very good information.
Thanks.
Hello! I’ve been reading your web site for some time now and finally got the courage to go ahead and give you
a shout out from Dallas Tx! Just wanted to mention keep up the great job!